Transmission Media
Transmission media is the medium that carries the information from sender to receiver. Information is transmitted normally through electrical or electromagnetic signals.
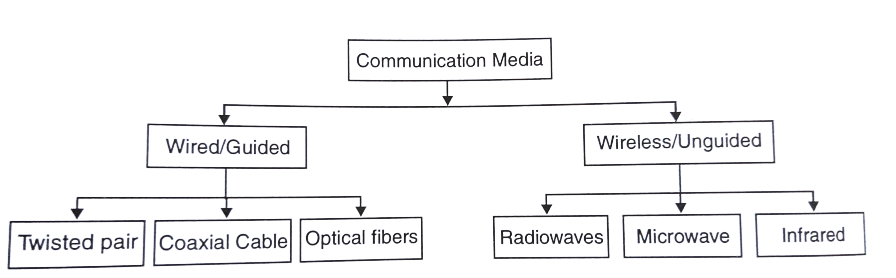
Types of Transmission Media
A Transmission media is broadly classified into two groups
- Wired or guided Media
- Wireless or unguided Media
Wired or guided Media:-
It is a media that contain some conducting material or metal to carry data or signal. Many types of cables and wires fall under this category. Each of them has its own unique characteristics, such as transmission speed, noise resistance, physical design, and cost. It includes copper wires twisted pair, coaxial cable and optical fibers.
Twisted Pair:– A twisted pair consists of two copper wires about 1 mm thick. These two wires are individually contained in a plastic insulation and are twisted together in a helical form. Polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, flouropolymer resin and Teflon(r) are some of the substances that are used for insulation purposes.
Types of Twisted Pair
- Unshielded twisted pair
- Shielded twisted pair
Coaxial Cable:- Coaxial cables are the guided media that carries the signal of higher frequency range compared to twisted pair cable. The frequency range of coaxial cable is 100kHz to 500 MHz. Coaxial cables are also called coaxial .It consists of one central copper wire that is covered with a plastic insulator called a dielectric.
Types of Coaxial Cable
- Baseband
- Broadband
Optical Fiber:- Optical Fiber cable is made of glass or plastic and transmits the signals in the form of light. An optical transmission system has three basic components.
- Light Source
- Transmission medium
- Detector
Light Source:- A light source, such as an LED or laser beam, is used to indicate a bit 1 with a pulse of light and a bit 0 with the absence of light.
Transmission Medium:- The transmission medium for this system is an ultra-thin fiber of glass.
Detector:- A detector is used to generate an electrical pulse when the light falls upon it.
Wireless or unguided Media Guided media:-
Wireless media transports electromagnetic waves without using a physical conductor. Signals are broadcast through air and are available to anyone who has a device capable of receiving them.
There are different ways in which unguided signals can travel from sources to destination:-
- Ground propagation: Radio waves travel through lowest portion of atmosphere close to the earth. These are the low frequency signals that travel in all the directions from transmitting antenna and follow the curvature of earth.
- Sky propagation: In this method, high frequency radiowaves are radiated upward into ionosphere. From ionosphere these signals are reflected back to the surface of $2 earth. Ionosphere is the atmospheric layer where the particles exist as ions.
- Line-of-sight propagation: This method uses very high frequency signals that are transmitted in a straight line path from one antenna to another. It requires proper placement of antennas in terms of their heights and distance.
Radiowaves Transmission Media:- Radio waves have frequency between 3KHz and 1GHz. Radiowaves are omni directional i.e they travel in all the directions from the source. Because of this property, transmitter and receiver need not to be aligned. They can penetrate buildings easily so they are widely use for communication both indoors and outdoors.
Microwave Transmission Media :- Microwaves are electromagnetic waves having frequencies between 1GHz and 300GHz. There are two types of microwave data communication systems:
- Terrestial microwave system
- Statellite microwave system
Infrared Waves:- Electromagnetic waves having frequencies from 300GHz to 400THz are called IR waves or Infrared waves. IR waves used for short range communication and use line-of-sight propagation. IR waves used for communication between keyboard, mouse and printers. The most common application of IR waves is remote control used for TV, DVD players and stereo system.
How bridge is different from gateway?
Bridge networks are distinct from gateway networks in several ways. Bridges are used to connect two separate LANs, while gateways are used to connect two different networks, such as a LAN and a WAN. Bridges are data link layer devices, while gateways are network layer devices. Bridges are used to filter and forward packets based on MAC addresses, while gateways use IP addresses to forward packets. Additionally, bridges are used to connect two similar networks, while gateways are used to connect two dissimilar networks.




This isn’t just writing; it’s a beautiful exploration of thought, full of insights that feel like small revelations.